淺談JavaScript中你可能不知道URL構(gòu)造函數(shù)的屬性
URL
URL 是統(tǒng)一資源定位符,對(duì)可以從互聯(lián)網(wǎng)上得到的資源的位置和訪問(wèn)方法的一種簡(jiǎn)潔的表示,是互聯(lián)網(wǎng)上標(biāo)準(zhǔn)資源的地址。互聯(lián)網(wǎng)上的每個(gè)文件都有一個(gè)唯一的 URL,它包含的信息指出文件的位置以及瀏覽器應(yīng)該怎么處理它,
在 Web 開(kāi)發(fā)中,有許多情況需要解析 URL,這篇主要學(xué)習(xí)如何使用 URL 對(duì)象實(shí)現(xiàn)這一點(diǎn)
例如,這里是這篇博客文章的路徑:
https://www.vipbic.com/thread.html?id=101
通常您需要訪問(wèn) URL 的特定屬性。這些可能是主機(jī)名(例如 vipbic.com ) ,或者路徑名(例如/thread)
JavaScript用于訪問(wèn)URL對(duì)象的提供一個(gè)URL()構(gòu)造函數(shù),很方便解析
一個(gè)完整URL
用一張圖片來(lái)解釋?zhuān)瑳](méi)有太多的文字描述,在下面的圖片中你可以找到一個(gè) URL 的主要包含屬性:
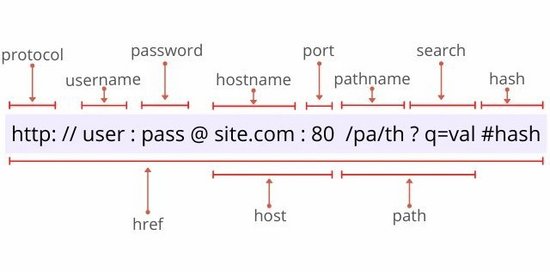
URL constructor
URL ()是一個(gè) constuctor 函數(shù),它可以解析 URL 的對(duì)象:
const url = new URL(relativeOrAbsolute [, absoluteBase]);
relativeOrAbsolute參數(shù)可以是絕對(duì) URL,也可以是相對(duì) URL。如果第一個(gè)參數(shù)是相對(duì)的,那么第二個(gè)參數(shù) absoluteBase 必須是絕對(duì) URL,它必須是第一個(gè)參數(shù)的基礎(chǔ)
例如,讓我們用一個(gè)絕對(duì) URL 初始化 URL():
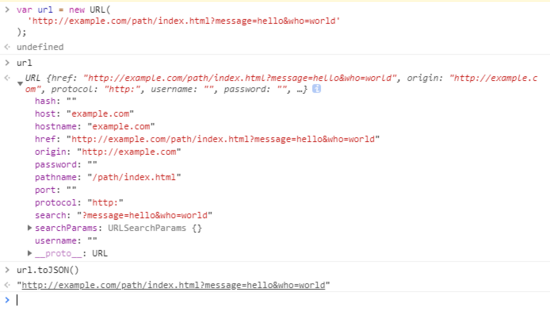
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html’);url.href; // => ’http://example.com/path/index.html’
或者合并相對(duì)和絕對(duì)的 url:
const url = new URL(’/path/index.html’, ’http://example.com’);url.href; // => ’http://example.com/path/index.html’
創(chuàng)建 URL ()實(shí)例后,可以訪問(wèn)實(shí)例:
interface URL { href: USVString; protocol: USVString; username: USVString; password: USVString; host: USVString; hostname: USVString; port: USVString; pathname: USVString; search: USVString; hash: USVString; readonly origin: USVString; readonly searchParams: URLSearchParams; toJSON(): USVString;}
可以嘗試在瀏覽中打印
Query string
Search 屬性訪問(wèn)前綴為? : 的 URL 的查詢(xún)字符串:
const url = new URL( ’http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world’);url.search; // => ’?message=hello&who=world’
如果查詢(xún)字符串不存在的字符串,url.search 將返回為空字符串” :
const url1 = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html’);const url2 = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html?’);url1.search; // => ’’url2.search; // => ’’
Parsing query string

訪問(wèn)查詢(xún)參數(shù)比訪問(wèn)原始查詢(xún)字符串更方便
一種簡(jiǎn)單的查詢(xún)參數(shù)選擇方法提供了 url.searchParams 屬性,該屬性包含 URLSearchParams 的實(shí)例
URLSearchParams 對(duì)象提供了許多方法(如 get (param)、 has (param))來(lái)訪問(wèn)查詢(xún)字符串參數(shù)
看一個(gè)例子:
const url = new URL( ’http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world’);url.searchParams.get(’message’); // => ’hello’url.searchParams.get(’missing’); // => null
get.(’message’),返回消息查詢(xún)參數(shù)的值-‘ hello’,當(dāng)去嘗試,訪問(wèn)一個(gè)不存在的參數(shù) url.searchParams.get(’missing’)的結(jié)果為 null
hostname
Hostname 屬性包含 URL 的主機(jī)名:
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html’);url.hostname; // => ’example.com’
pathname
屬性獲取 URL 的路徑名:
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html?param=value’);url.pathname; // => ’/path/index.html’
如果 URL 沒(méi)有路徑,URL.pathname 屬性將返回斜杠字符/:
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/’);url.pathname; // => ’/’
hash
可以使用 url.hash 屬性訪問(wèn)#后面的參數(shù):
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html#bottom’);url.hash; // => ’#bottom’
當(dāng) URL 中的散列#時(shí),URL.hash 計(jì)算為空字符串” :
const url = new URL(’http://example.com/path/index.html’);url.hash; // => ’’
URL validation
當(dāng)new URL ()構(gòu)造函數(shù)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)實(shí)例時(shí),作為副作用,它還驗(yàn)證 URL 的正確性。如果 URL 值無(wú)效,則拋出 TypeError
例如,http ://example. com 是一個(gè)無(wú)效的 URL,因?yàn)?http 后面的空格字符
讓我們使用這個(gè)無(wú)效的 URL 來(lái)初始化解析器:
try { const url = new URL(’http ://example.com’);} catch (error) { error; // => TypeError, 'Failed to construct URL: Invalid URL'}
因?yàn)椤痟ttp ://example. com’是一個(gè)無(wú)效的 URL,正如預(yù)期的那樣,new URL (’http ://example. com’)拋出一個(gè) TypeError
URL manipulation
除了訪問(wèn) URL 屬性之外,搜索、主機(jī)名、路徑名、hash等屬性都是可寫(xiě)的??因此您可以操作 URL
例如,讓我們把現(xiàn)有 URL 的主機(jī)名從 red. com 修改為 blue.io:
const url = new URL(’http://red.com/path/index.html’);url.href; // => ’http://red.com/path/index.html’url.hostname = ’blue.io’;url.href; // => ’http://blue.io/path/index.html’
注意,只有 URL ()實(shí)例的 origin 和 searchParams 屬性是只讀的。其他的都是可寫(xiě)的,當(dāng)你改變它們的時(shí)候可以修改 URL
總結(jié)
URL()構(gòu)造函數(shù)可以方便地在 JavaScript 中解析(和驗(yàn)證) URL
new URL (relativeOrAbsolute [ ,absolute base ])接受作為第一個(gè)參數(shù)的絕對(duì)或相對(duì) URL。如果第一個(gè)參數(shù)是相對(duì)的,則必須將第二個(gè)參數(shù)指
示為一個(gè)作為第一個(gè)參數(shù)基礎(chǔ)的URL
創(chuàng)建 URL()實(shí)例后,可以獲取到以下實(shí)列方法
url.search 原始查詢(xún)字符串 url.searchParams 選擇查詢(xún)字符串參數(shù) url.hostname 訪問(wèn)主機(jī)名 url.pathname 讀取路徑名 url.hash #后面的參數(shù)文章屬于翻譯,作者部分有所改動(dòng),
作者:羊先生
英文原文, https://dmitripavlutin.com/parse-url-javascript/
到此這篇關(guān)于淺談JavaScript中你可能不知道URL構(gòu)造函數(shù)的屬性的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)JavaScript URL構(gòu)造函數(shù)內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. IntelliJ IDEA配置Tomcat服務(wù)器的方法2. Docker 部署 Prometheus的安裝詳細(xì)教程3. IntelliJ IDEA導(dǎo)入jar包的方法4. VMware中如何安裝Ubuntu5. 使用 kind 和 Docker 啟動(dòng)本地的 Kubernetes環(huán)境6. IntelliJ IDEA調(diào)整字體大小的方法7. IntelliJ IDEA恢復(fù)刪除文件的方法8. IntelliJ IDEA創(chuàng)建web項(xiàng)目的方法9. IntelliJ IDEA設(shè)置背景圖片的方法步驟10. IntelliJ IDEA刪除類(lèi)的方法步驟
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備