java8新特性之日期時(shí)間API

long times = System.currentTimeMillis();//返回的是當(dāng)前時(shí)間與1970年1月1月1日0分0秒之間以毫秒為單位的時(shí)間差//稱為時(shí)間戳System.out.println(times);
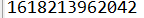

將java.util.Date 對象轉(zhuǎn)換為java.sql.Date對象:
//將java.util.Date 對象轉(zhuǎn)換為java.sql.Date對象Date date1 = new Date();java.sql.Date date2 = new java.sql.Date(date1.getTime());三、java.text.SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat是對日期Date類的格式化和解析。

兩個(gè)操作:
1.格式化:
將日期轉(zhuǎn)換為字符串:
SimpleDateFormat sfd = new SimpleDateFormat();Date date = new Date();System.out.println(date);String formateDate = sfd.format(date);System.out.println(formateDate);

也可以指定具體的格式化格式,查看具體的API格式。例:指定格式的格式化輸出(調(diào)用帶參數(shù)的構(gòu)造器)
Date date = new Date();System.out.println(date);SimpleDateFormat sfd = new SimpleDateFormat('yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss');String formateDate = sfd.format(date);System.out.println(formateDate);
2.解析:
將 字符串 轉(zhuǎn)換為 日期。即格式化的逆過程。
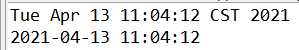
String str = '2021/4/12 下午10:16'; SimpleDateFormat sfd = new SimpleDateFormat();Date date2 = sfd.parse(str);System.out.println(date2);
這個(gè)注意要拋異常(傳入的str格式要與Date的原格式一致,或者說要與SimpleDateFormate當(dāng)前識別的格式相同)。
練習(xí):將字符串“2021-04-13” 轉(zhuǎn)換為java.sql.Date類型對象。
分析:首先將字符串解析為Date類型的對象,然后在轉(zhuǎn)為java.sql.Date類型對象。
public static void testExper() throws ParseException {String s = '2021-04-13';SimpleDateFormat sfd = new SimpleDateFormat('yyyy-MM-dd');Date date = sfd.parse(s);java.sql.Date date2 = new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());System.out.println(date2);}
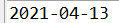

常用實(shí)例化方法:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();System.out.println(calendar.getClass()); //java.util.GregorianCalendar,其實(shí)還是子類類型的對象
常用方法:
1.get():獲取常用的屬性和信息。2.set():設(shè)置:相當(dāng)于把本身的日期給改變了3.add():添加(增加時(shí)間、天數(shù))4.getTime():日歷類----> Date類5.setTime():Date類----> 日歷類
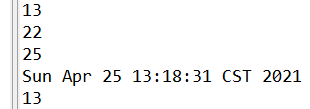
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();//System.out.println(calendar.getClass()); //java.util.GregorianCalendar//get()int days = calendar.get(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//獲取當(dāng)前日期是這個(gè)月的第幾天System.out.println(days); //13//set()calendar.set(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 22);//重新設(shè)置 days = calendar.get(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//在重新獲取System.out.println(days); //22//add()calendar.add(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 3);days = calendar.get(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days); //25//getTime():日歷類----> Date類Date date = calendar.getTime();System.out.println(date); //Sun Apr 25 13:14:59 CST 2021//setTime():Date類----> 日歷類Date date2 = new Date();calendar.setTime(date2);days = calendar.get(calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);System.out.println(days); //13
新日期時(shí)間API出現(xiàn)的背景:
可變性:像日期和時(shí)間這樣的類應(yīng)該是不可變的。偏移性:Date中的年份是從1900開始的,而月份都是從0開始。格式化:格式化只對Date有用,Calendar則不行。
此外,他們也不是線程安全的;不能處理閏秒。


說明:LocalDateTime類相較于其他兩個(gè)類使用頻率較高。

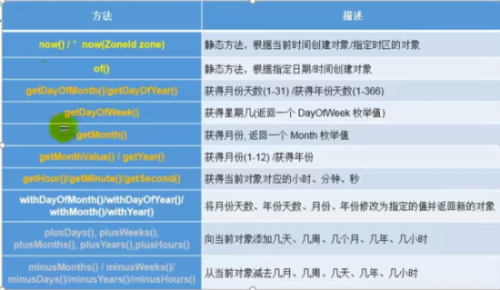
(1)now():獲取當(dāng)前的日期、時(shí)間、日期+時(shí)間。(實(shí)例化方法一)
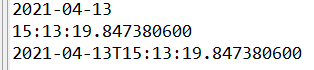
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println(localDate);System.out.println(localTime);System.out.println(localDateTime);
(2)of():設(shè)置指定時(shí)間的年、月、日、時(shí)、分。沒有偏移量。(實(shí)例化方法二)
//of():設(shè)置指定時(shí)間的年、月、日、時(shí)、分。沒有偏移量。LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(2021, 4, 13, 15, 20);System.out.println(localDateTime2);
(3)getXxx():獲取…(4)withXxx():修改(設(shè)置)…,這個(gè)方法不會改動(dòng)原本的值。(5)plusXxx():添加(6)minusXxx():減
三、Instant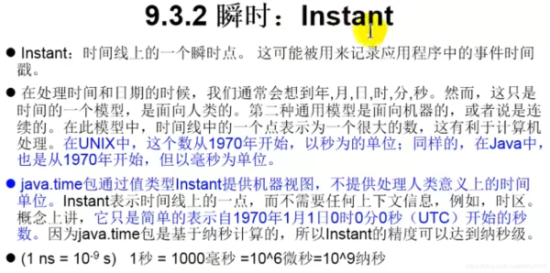
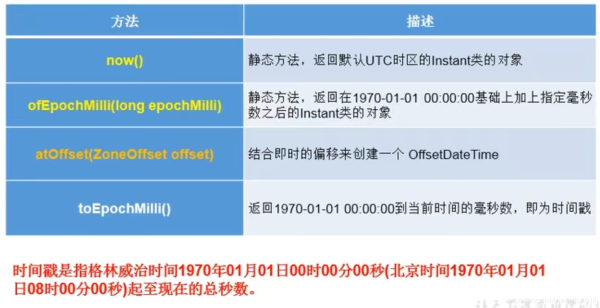
(1)now():獲取本初子午線對應(yīng)的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)時(shí)間。(實(shí)例化方法一)
//now():獲取本初子午線對應(yīng)的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)時(shí)間Instant instant = Instant.now();System.out.println(instant);//添加時(shí)間的偏移量OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));System.out.println(offsetDateTime);
(2)toEpochMilli():獲取毫秒數(shù)
long milli = instant.toEpochMilli();System.out.println(milli);
(3)ofEpochMilli():通過給定的毫秒數(shù),獲取Instant實(shí)例 (實(shí)例化方法二)
//通過給定的毫秒數(shù),獲取Instant實(shí)例Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1618300028028l);System.out.println(instant2);四、DateTimeFormatter類
DateTimeFormatter類:格式化或解析日期、時(shí)間,類似于SimpleDateFormat。

(1)預(yù)定義的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)格式進(jìn)行格式化:DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME
注意: 日期-----> 字符串
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();String str = formatter.format(localDateTime);//注意類型變化System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(str);
(2)本地化相關(guān)的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime()。
//FormatStyle.SHORT / FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM :適用于LocalDateTime
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();String str = formatter.format(localDateTime);System.out.println(localDateTime);System.out.println(str);

(3)自定義格式:ofPattern()
//自定義格式。如:DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern('yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss');String string = formatter.format(LocalDateTime.now());System.out.println(string);

到此這篇關(guān)于java8新特性之日期時(shí)間API的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java日期時(shí)間API內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. IntelliJ IDEA導(dǎo)入jar包的方法2. SSM框架JSP使用Layui實(shí)現(xiàn)layer彈出層效果3. 刪除docker里建立容器的操作方法4. IntelliJ IDEA導(dǎo)出項(xiàng)目的方法5. Java源碼解析之ClassLoader6. JS如何在數(shù)組指定位置插入元素7. .Net中的Http請求調(diào)用詳解(Post與Get)8. PHP下對緩沖區(qū)的控制9. java使用xfire搭建webservice服務(wù)的過程詳解10. python 調(diào)用API接口 獲取和解析 Json數(shù)據(jù)

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備